[4회차-①] JAVA (배열)
강의명 : 오픈프레임워크를 활용한 디지털 융합 SW엔지니어 양성 과정
강의 날짜 : 21.03.26
<난수 프로그램>
//for루프를 사용하여 0부터 99사이의 난수의 합을 계산하는 프로그램
package march36th;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RandomNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random generator=new Random(); //난수를 반환하는 클래스가 자바에 존재
Scanner index = new Scanner(System.in);
int count; //난수의 개수를 저장하는 변수
int sum=0; //합을 저장할 변수
int number; // 랜덤넘버를 저장할 변수
System.out.print("난수의 개수 : ");
count=index.nextInt(); //사용자가 개수를 입력
for(int i=0;i<count;i++) {
number=generator.nextInt(100); // 랜덤넘버 반복 생성하여 number변수에 저장
sum+=number; //sum에 누적하여 합을 구함
}
System.out.print("난수 "+count+"개의 합은 "+sum);
}
}1. java.util.Random
Random (변수명) = new Random();
변수명.nextInt(파라미터)
→ 0 ~ (파라미터-1) 까지 랜덤의 정수가 반환된다.
2. java.util.Math
(int)(Math.random() * 최대값)+최소값
<배열>
배열(Array) : 동일한 타입의 변수들의 모임
배열은 변수들을 모아놓은 것이다. 하나의 이름을 공유한다.
대량의 데이터의 경우는 배열로 표현하는 것이 편리하다.
1. 배열의 생성
① 배열의 참조 변수를 선언 → 참조변수? 주소를 가지고 있는 것! 객체를 가리키고 있는 변수
(자료형)[] (변수명);
② new 연산자를 사용하여 생성
변수 = new (자료형)[(자료의 크기)];
2. 배열의 인덱스
배열의 요소에는 번호가 붙어 있는데 이것이 인덱스(index)이다.
대괄호 안에서 표시해주며, 인덱스의 최대값은 (배열의 크기-1)이다.
package march36th;
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] s=new int[10]; //배열 선언
int i; //반복문을 돌리기 위한 변수 선언
for(i=0;i<s.length;i++) s[i]=i; //베열의 크기만큼 반복하면서 차례대로 숫자를 저장
for(i=0;i<s.length;i++) System.out.print(s[i]+" "); //순서대로 출력
}
}
*배열의 크기를 정해주기 전에 초기화를 해주고 나서 확인을 해주면 배열의 크기가 저절로 정해졌음을 확인할 수 있다.
//배열에 원소를 초기화하여 크기 설정하기
package march36th;
public class ArrayTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] scores= {10,20,30,40,50}; //먼저 배열에 원소 초기화
for(int i=0; i<scores.length;i++) {
System.out.print(scores[i]+ " "); //배열의 크기만큼 반복하면서 출력
}
}
4. 무명 배열
이름을 정해주지 않은 배열로 한 번만 사용하고 사용하지 않는다.
//무명 배열
package march36th;
public class AnonymousArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("숫자들의 합 : "+
sum(new int[] {1,2,3,4})); //무명배열은 선언할 때만 쓰이고 쓰이지 않음
}
public static int sum(int[] numbers) { //정수 배열을 파라미터로 받는 sum 메소드 선언
int total =0;
for(int i =0; i<numbers.length;i++) {
total = total +numbers[i];
}
return total;//합계 반환
}
}
4. 탐색
*순차 탐색
배열의 원소를 순서대로 하나씩 꺼내서 탐색키와 비교하여 원하는 값을 찾아가는 벙법
//값 탐색 프로그램
package march36th;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SeqSearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int s[]= {0,10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100};//배열 초기화
int value,ind=-1;//탐색할 값을 저장할 변수, 인데스를 저장할 변수 선언
Scanner index=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("탐색할 값을 입력하시오 : ");
value = index.nextInt();
for(int i =0;i<s.length;i++) {
if(s[i]==value) ind=i;
}
if(ind<s.length&&ind>=0)
System.out.printf(" %d값은 %d 위치에 있습니다.\n",value,ind);
else System.out.println("값을 찾을 수 없습니다."); //값을 찾지 못하면 인덱스는 -1
}
}
5. for-each 루프
for ( 변수명 : 배열의 변수명 )
변수에는 첫 번째 배열 원소부터, 마지막 배열 원소까지 차례대로 대입된다.
6. 배열 참조 변수의 복사
* System.arraycopy(복사할 배열, 복사할 첫 위치, 대상 배열, 붙여 넣을 첫 위치, 복사할 요소 개수)
//배열의 복사
package march36th;
public class ArrayCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array1= {10,20,30,40,50};
int[] array2= {1,2,3,4,5};
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array2, 0, 5); // array1을 인덱스 0부터 5개의 요소를 array2의 인덱스 0로 복사
for(int i=0;i<array2.length;i++) {
System.out.println(array2[i]);
}
}
}

7. args 변수 사용하기
package march36th;
public class CommandLine {
//메인함수의 파라미터 args사용하기
public static void main(String[] args) { // 문자열 배열 args
if(args.length>0) {
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++) {
System.out.print(" "+args[i]);
}
if(args[0].equals("-h"))
System.out.print("HELP");
}
}
}그냥 돌리면 아무것도 출력되지 않는다.

Run As- Run configurations 선택
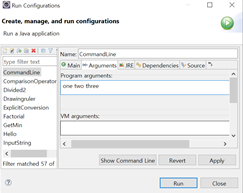
Program arguments에
"one two three" 를 입력하고, Run을 선택한다.
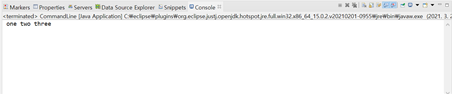
실행창에 one two three가 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있다!
8. 정렬
* Arrays.sort(배열명)-> 순서대로 정렬
//함수를 사용해 정렬하기
package march36th;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int size=10;
int[] num=new int[size];
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) {
int r=(int)(Math.random()*100);//랜덤으로 배열 생성
num[i]=r;
}
System.out.print("최초의 리스트: ");
for(int r : num)
System.out.print(r+" ");
Arrays.sort(num);//정렬
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정렬된 리스트: ");
for(int r:num)
System.out.print(r+ " ");
}
}
9. 이차원 배열
n*m행렬로 표현 될 수 있는 배열의 집합이다.
//이차원 배열 출력하기
package march36th;
public class ArratTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [][] array= {
{10,20,30,40},
{50,60,70,80},
{90,100,110,120}};//이차원 배열 초기화
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<array.length;i++) { //행의 개수
for(j=0;j<array[i].length;j++) { //열의 개수
System.out.println(i+"행"+j+"열"+array[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
10. ArrayList 클래스
배열의 크기를 정하지 않고 사용할 수 있어서 편리하다.
뒤에서 또 다룰 것이니 기억해둘 것.
* ArrayList<사용할 객체의 자료형> (배열명) = new ArryList<사용할 객체의 자료형>();
* (배열명).add(); //요소값을 추가하는 메서드
* (배열명).get(인덱스); //요소를 가져오는 메서드
package march36th;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Book> library=new ArrayList<Book>();
library.add(new Book("태백산맥","조정래"));
library.add(new Book("데미안","헤르만 헤세"));
library.add(new Book("어떻게 살 것인가","유시민"));
library.add(new Book("토지","박경리"));
library.add(new Book("어린왕자","생택쥐베페리"));
library.add(new Book("인간실격","다자이 오사무"));
int i;
for(i=0;i<library.size();i++) {
Book book=library.get(i);
book.showBookInfo();
}
library.remove(3);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("향상된 방법");
for(Book book:library) {
book.showBookInfo();
}
}
}